Periodontitis, also known as Dental pyorrhea, is a disease of the gums. It is a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the oral mucosa around the teeth and is caused by bacterial microorganisms. This is a gum infection where the gums pull away from the teeth, resulting in bone loss, loose teeth, or complete tooth loss.
The initial stage of Periodontal Disease is known as gingivitis, in which the gums become swollen, red and sensitive leading to bleeding gums. Gingivitis further develops into periodontitis (Pyorrhea Disease). This dental problem is mostly seen in adults.

Periodontitis (Gum Disease): Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Pyorrhea can be of the following types.
1. Gingivitis
The most typical type of pyorrhea is this one. In this condition, the gums may swell and appear red. During the daily cleaning of the teeth, blood can also come out of them.
2. Mild Periodontitis
If untreated, gingivitis can cause mild pyrexia. In this situation, the gums start leaving their place around the teeth. This can lead to rapid loss of bone around the teeth.
3. Advanced Periodontitis
This is the most serious condition of gum disease. In this, the bones supporting the teeth start getting damaged. At the same time, the teeth start becoming loose.
Do you know : What is Angina Types and Treatment?
Symptoms of Periodontal Disease.
Symptoms of Periodontitis includes :
• Bad breath or halitosis
• Gingival recession
• Swollen gums
• Bleeding gums
• Gum discoloration: – Bright red, dark red or purple gums
• soft gums
• Losing teeth
• Tooth sensitivity
• Deep pockets, known as periodontal pockets, form between the gums and teeth.
• Pus around the teeth and gums
• Difficulty in chewing food
• Spitting up blood when brushing or flossing teeth
Causes and Risks For Periodontal Disease
Causes of Periodontal Disease include:

• Accumulation of bacterial micro-organisms in the mouth can lead to periodontitis. There are many healthy bacteria in the oral cavity. But some bacteria combine with mucus and other foods to form a sticky film on the surface of the teeth called dental plaque.
• Plaque can be readily eradicated if dental hygiene is practised regularly. But if the teeth are not cleaned properly, the plaque hardens and takes the form of tartar (calculus). Only a dentist or dental hygienist can remove this tartar from the teeth.
• Buildup of plaque and tartar leads to gingivitis (gum disease). This includes swelling and bleeding gums. It can be treated with dental care and cured by following good dental hygiene practices at home. If this gum disease is not treated, it will eventually turn into periodontitis.
• If this gum disease is not treated, it will eventually turn into periodontitis.
Risk Factors :
Factors that can affect gum health and increase the risk of periodontitis include-
• Swelling of gums
• Wrong oral care habits
• Smoking
• Chewing tobacco
• Hormonal changes in women (related to pregnancy or menopause)
• Obesity
• Vitamin C deficiency
• Genetics
• Some medicines can cause dry mouth or gum problems.
• Some conditions can cause low immunity, such as leukemia, HIV/AIDS, and cancer treatment.
• Certain diseases, eg, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, osteoporosis, and Crohn’s disease.
Diagnosis and Treatment For Periodontal Disease
Your dentist may do the following or order some tests to determine if you have periodontitis and how severe it is.
• The dentist will inquire about the medical history (any previous dental treatment), eating habits and medications to identify any contributing factors that may be causing the dental disease
• The dentist will do a thorough examination of the teeth and gums in the mouth to look for plaque and tartar buildup and gum problems.
• The dentist will measure the depth of the periodontal pocket around each tooth with a periodontal probe to determine whether periodontal disease is present and how far it has progressed. A gum pocket deeper than 4 mm may indicate periodontitis. Pockets more than 5 mm deep are difficult to clean.
• Dental X-rays can help a dentist identify bone loss, gum disease and damage to tooth structure at an early stage.
Treatment :
If the gum infection is in its early stages, periodontitis treatment may involve less invasive procedures. It includes –
1. Scaling:
It is a common dental procedure to remove plaque and tartar from the surfaces of teeth and below the gum line. This can be done using handheld instruments such as a dental scaler and curette or a laser or ultrasonic device.
2. Route Planning:
3. Antibiotics:
Surgical Treatment For Periodontal Disease
In case of advanced periodontitis, dental surgery may have to be done. It includes –
1. Flap Surgery (Pocket Reduction Surgery)
It is also known as gingivectomy or osseous surgery. It is a dental surgery to clear the bacteria present in the space between the gums and teeth in case of advanced stage of periodontitis.
2. Soft Tissue Graft
Soft tissue grafting is used to protect the tooth root by adding tissue to cover the roots from a donor source, usually the roof of the mouth or adjacent gum tissue.
3. Changes in Bones
Bone loss and tooth loss are health concerns of older men and women. Tooth loss a ects approximately 1 in 3 adults over age 65. If you have osteoporosis, you may be at risk for tooth loss. When the jawbone becomes less dense tooth loss can occur.
4. Guided Tissue Regeneration
GTR is an advanced procedure that uses an artificial membrane to act as a barrier. The use of the barrier allows only new growing tissues and bone into the area and prevents any unwanted fast-growing tissues from migrating to the tooth and underlying bone.
5. Tissue-Stimulating Proteins
Another technique involves applying a special gel to a diseased tooth root. This gel contains the same proteins found in developing tooth enamel and stimulates the growth of healthy bone and tissue.
What To Do and What Not to Do.
Periodontitis is a gum infection that causes inflammation of the soft gum tissue and results in damage to the tooth structure. It is triggered by the growth of dental plaque, a bacteria found on the surfaces of teeth. If it is left untreated in the later stages, it can lead to gingivitis, which will eventually turn into periodontal disease.
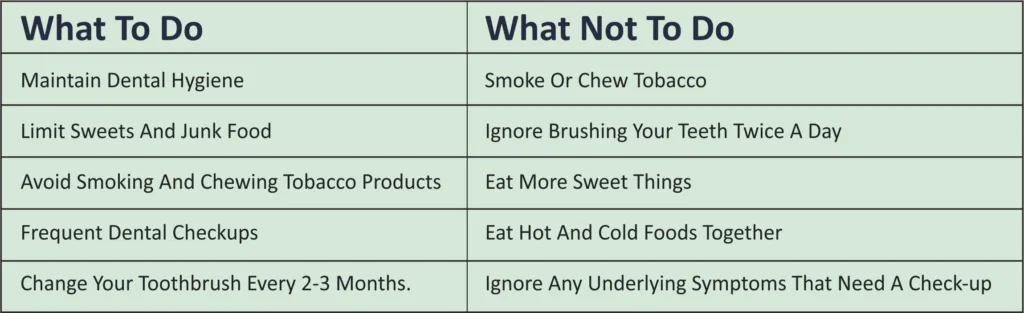
Preventions – Good Habits Should Accept
Periodontitis can be prevented by practicing good oral hygiene and having regular dental checkups.
Good Oral Hygiene – This includes :
1. Daily Brushing
• As we all know that it is necessary to brush our teeth twice daily, as it cleans our teeth and keeps bacteria free. The number of bacteria in our mouth is highest in the morning, so we must brush in the morning.
• We must brush our teeth even before sleeping at night.
• Usually people do not know the right way of brushing, due to which their teeth are not cleaned properly.
• Too hard brush should not be used, it wears away the layer of the teeth and causes the problem of sensitivity in the teeth and also causes gum disease.
• We should always use soft brush.
• The brush should always be moved on the teeth in small circular motions back and forth and upwards with light hands.
2. Floss Once Daily
• Even after brushing, we should use floss in those parts of our teeth where our brush cannot reach or in the space between the teeth, where small particles of food get accumulated.
• Apart from cleaning our teeth, it also removes problems like bad breath.
3. Use Mouthwash
• Using mouthwash half an hour after brushing gives the right result.
• Along with our teeth, it removes problems like gum problems, foul smell of tongue and gums.
• Gargle with mouthwash for 30 seconds. Do this twice a day.
4. Use Fluoride
• Fluoride is made from fluorine. It is an element of soil. It protects our teeth from decay.
• It is found in drinking water and is also present in toothpaste.
5. Do not smoke and consume tobacco.
• Tobacco use and smoking are really bad for our health. It damages our lungs and is also extremely harmful for teeth and gums.
• It slows down and weakens the healing process in our gums.
• Yellows the tongue, the inside of the mouth and the teeth.
• The risk of oral cancer is high due to excessive smoking and tobacco use.
6. Drink Plenty of Water
• The most significant beverage in our lives is water.
• Drinking water helps in keeping our teeth and gums clean along with the body.
• It cleans out the tiny particles of food stuck between our teeth.
7. Make Sure to Eat Fruits and Vegetables
• Fruits and vegetables help in keeping our teeth clean and providing nutrition to the gums and teeth, such as apples, carrots, celery and leafy vegetables, etc.
• There are many fruits and vegetables, which are rich in Vitamin C and antioxidants. She keeps our gums and oral tissue healthy.
• Also protects our teeth and gums from bacterial infection.
Home Remedies for Periodontitis

There are many types of home remedies available for pyorrhea, which are discussed below. Also, Let’s be clear that the problem can only be solved with the aid of these home remedies. On the other hand, if the illness is severe, these treatments might not work as well. It is essential to see a doctor for a checkup in this situation.
1. Baking Soda
Pyorrhea can also be treated with baking soda. Baking soda contains a quality known as dentifrices, according to a scientific research published by NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information). This property can help reduce plaque and gingivitis from teeth, which can help avoid the risk of pyorrhea.
How to use:
• Take a small spoon of baking soda.
• Add a few drops of water to it now to turn it into a paste.
• Now with the help of toothpaste, clean your teeth with it.
• This process can be used once in two weeks.
• Before using it, you can, if you’d like, seek medical counsel.
2. Salt
Additionally, salt can aid in the treatment of pyorrhea. Although salt has been used for a long time to cure pyorrhea, there are scientific justifications for it. Actually, anti-inflammatory properties are found in salt. Due to this property, it can help in the treatment of pyorrhea by reducing the swelling of the gums.
How to use:
• Take a small spoon of salt.
• Now mix two-three drops of mustard oil in it and make a paste.
• After that, use this paste to brush your teeth and gums with a gentle brush.
• You can apply this therapy once each week.
3. Coconut Oil
Coconut oil can also be useful to remove the problem of pyorrhea. Actually, coconut oil contains lauric acid. The anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial effects of this acid. Because of this, utilising coconut oil can aid in the treatment of the plaque-related issue of increased pyorrhea. Oil pulling method is used for this.
How to use:
• Mix 5-6 drops of coconut oil in a cup of water.
• Then put this mixture in the mouth and move it well in the whole mouth.
• Keep it in the mouth for about 4-5 minutes.
• Then by taking it out of the mouth, clean the mouth through mouthwash.
• It can be used once a week on medical advice.
Note – Cleaning the teeth through oil pulling with coconut oil can also have some side effects, therefore, instead of using this, other treatment method mentioned in the article can be adopted. In addition, you might seek medical advice.
(Disclaimer: This article is for general information only. It is just to wake you up for your health purpose. Out intension is not to mislead or It cannot in any way be a substitute for any medicine or treatment. Always contact your doctor for more details.)
2 thoughts on “Periodontitis (Gum Disease) : Pyorrhea Symptoms, Causes, Treatment”