Heart Inflammation is how your heart reacts to injury or infection. For some people, heart inflammation occurs without warning. For others, it takes longer. Some people have severe symptoms, while others have hardly any symptoms. Inflammation severity might also differ from person to person depending on unique elements and causes. Below we’ll know more about Heart Inflammation, Types of Inflammation, Diagnose, Symptoms and Treatment.
Different Types, Causes, Recognizing Symptoms, Treatment Approaches, Preventive Measures
There are three types of heart inflammation that can affect a person, which are related to three different parts of the heart. The three types of inflammation of the heart are described below: –
1. Endocarditis :
It affects the lining in the heart chambers through which your blood passes and the valves that control the flow of blood from one chamber to another.
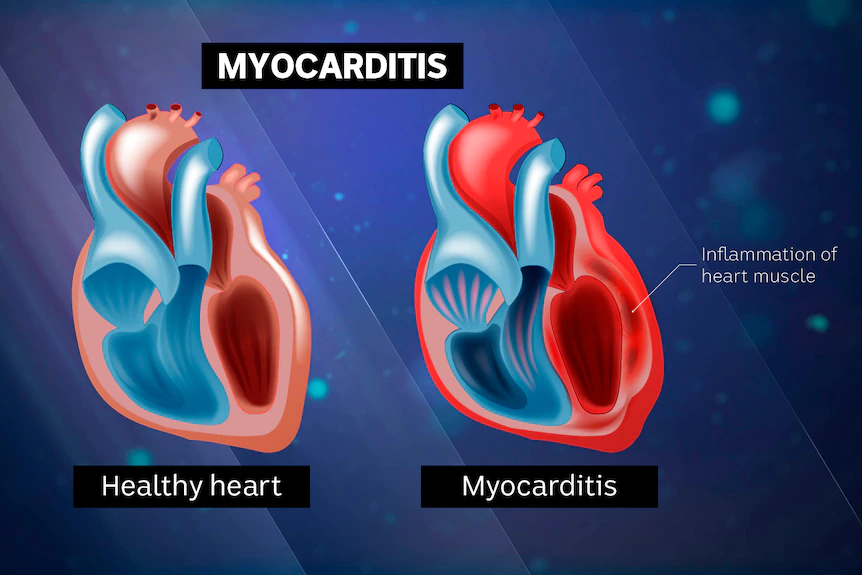
2. Myocarditis :
It affects the muscle that pumps your heart.
3. Pericarditis :
It affects the sac outside your heart.
How Does Heart Inflammation affect Our Body?
Inflammation of the heart can result in a variety of issues.
1. Endocarditis or Endocarditis :
Bacteria infect the lining of your heart valves. It can also travel to other parts of your body, infecting those areas as well.
2. Myocarditis:
When your heart muscle is inflamed, it has a more difficult time pumping blood.
3. Pericarditis :
The two layers of your pericardium thicken and brush against each other and your heart muscle.
Do you Know About Types of Heart Diseases?
What are the Symptoms of Heart Inflammation?
Common symptoms of all three types of heart inflammation include the following:
- Chest Pain.
- Difficulty in Breathing.
- Fever.
Depending on the type of heart inflammation you have, you may have other symptoms.
Symptoms of Endocarditis include:
- Pain in your stomach.
- Blood in your urine.
- Night sweats.
Symptoms of myocarditis include: - Swelling in your feet or legs.
- Nervousness of the heart.
- Extreme fatigue.
Symptoms of Pericarditis include:
- Fast heartbeat.
- Chest pain that gets better on sitting and bending forward.
When a virus is responsible for your heart inflammation, you may first notice symptoms of the virus, such as: - Runny nose.
- Cough.
- Stomach problem.
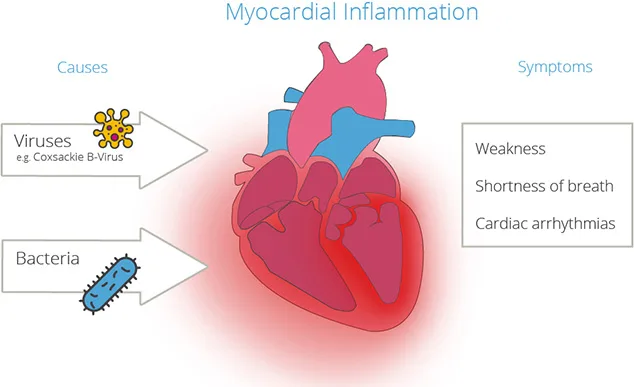
What are the Causes of Heart Inflammation?
Infection, usually from a virus or bacteria, causes most cases of inflammation of the heart. Other reasons include:
1. Autoimmune diseases like Rheumatoid Arthritis.
2. Things in your environment, such as Lead.
3. Medicines for Depression, Seizures or Weight Loss.
Some young adults have reported having myocarditis or pericarditis after receiving the COVID-19 Vaccination. However, most recovered after treatment with medicine.
Read Also : Is Type 2 Diabetes Curable?
How is Inflammation of the Heart Diagnosed?
Because the symptoms of inflammation of the heart depend on the type and vary from person to person, it is sometimes difficult to diagnose endocarditis, pericarditis, or myocarditis. A physical examination and test orders may be made by your doctor.
A. Physical Test
- To help diagnose heart inflammation, your healthcare provider, doctor, or investigator may ask some basic questions.
- Have you had endocarditis, myocarditis or pericarditis in the past?
- Have you had any illness or chest injury recently?
- Have you had any symptoms like fever, chest pain or shortness of breath?
- Do you have any other medical conditions or any other risk factors for edema of the heart, including exposure to certain drugs or toxins, or a travel history that may be important?
They might also carry out one or more of the below actions: - Check your legs for swelling which is a sign of heart failure.
- Check your skin for any changes, as may be seen in cases of endocarditis.
- Will check your temperature to determine if you have a fever.
- Will feel your abdomen, especially for a spleen that is larger than normal, or to determine if you have abdominal pain, which can occur with endocarditis.
- During examination listen to your heart for a new murmur that may be heard with endocarditis, a pericardial rub that may be heard with pericarditis, or an abnormal heart rhythm may be identified.
- Your lungs can be heard.
B. Imaging Tests and Procedures
1. Your doctor may need to do image tests or procedures to view your heart.
2. Heart imaging tests take pictures of your heart or its arteries or blood vessels to help your doctor see if there are any problems.
3. Endomyocardial Biopsy (EMB) examines very small pieces of the heart to look for myocarditis.
4. Heart Valve Tissue Test :
Identifies tiny germs or microbes from the heart valves or other growths found there that may be causing your endocarditis.
5. Pericardiocentesis :
Removes excess fluid in the pericardium, which is called a pericardial effusion. Your doctor will insert a needle or tube, called a catheter, into the chest wall to drain this extra fluid. Your doctor will look at the fluid for bacteria, signs of cancer, or other causes of pericarditis.
Do You Know Side Effects of Keto Diet?
C. Blood Tests
Your healthcare professional can utilise blood tests to identify the reason of your heart swelling.
1. Blood Cultures
Identify and treat the exact bacteria, virus, or fungus causing the infection in endocarditis or pericarditis.
2. Cardiac Troponin or Creatine Kinase-MB.
There are blood markers that increase when there is damage to your heart. Since there are no specific blood tests for myocarditis, these markers are useful for showing injury to the heart muscle. However, they also increase with a heart attack or heart failure and do not necessarily mean that you have myocarditis. In situations of subacute or chronic myocarditis, they are frequently normal.
3. C-reactive Protein (CRP) or Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR).
Higher than normal can indicate inflammation in the body.
4. Complete Blood Count
Check for elevated white blood cell numbers, which may point to an infection.
5. Serum Cardiac Autoantibodies (AAbs).
There are substances that your body can make when you have an autoimmune disease. These antibodies attack your heart muscle.
Treatment For Heart Inflammation?
Your doctor may prescribe one or more medications or procedures to treat heart inflammation, depending on the type and cause of heart inflammation.
A. Medicines
1. Endocarditis:
Antibiotics
Treats bacterial infections. Side effects of antibiotics depend on which antibiotic is used, but may include diarrhea, problems with hearing, balance, kidney or decreased white blood cell counts. Some of these side effects may not occur until after treatment has ended.
Antifungal Medicines Treats Infection
Sometimes your doctor may recommend lifelong oral antifungal treatment to prevent the infection from coming back. Possible side effects of antifungal medicines include allergic reaction, diarrhoea, dizziness, itching, blisters or hives, difficulty breathing, weight loss and yellowing of the skin and eyes called jaundice.
2. Myocarditis:
Corticosteroids
Decrease the activity of the body’s immune system. Myocarditis brought on by autoimmune conditions such as lupus may be treated with corticosteroids.
Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG) Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG).
Controls the body’s inflammatory and immunological reactions.
3. Pericarditis:
Medicines to Relieve Pain and Reduce Inflammation
These include colchicine, aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory tablets (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen. Side effects are primarily gastrointestinal and include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Corticosteroids
Decrease the activity of the body’s immune system. With pericarditis, corticosteroids are used only in people who are not responding to or cannot take NSAIDs.
Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG) Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG).
Helps control the body’s immune and inflammatory response if you have an autoimmune disorder such as lupus.
B. Procedures & Surgery
Your doctor may consider procedures and surgery to treat your heart inflammation.
1. Heart Surgery
Damage to the valves or surrounding heart tissue from endocarditis can be managed. This may involve removal of infected tissue or reconstruction of the heart, which involves repair or replacement of the affected valve.
2. Pericardiocentesis
Removes excess fluid in the pericardium (called pericardial effusion).
3. Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator or Pacemaker
Can control irregular heartbeat that does not go away after a short period of time.
4. Pericardiectomy
Surgery is done to remove the pericardium. This treatment is only recommended if medication or other treatments have not worked. It can be a successful option for people who have pericarditis that goes away and comes back or who have end-stage constrictive pericarditis, where the pericardium has thickened and scarred.
How to Prevent Heart Inflammation?
If you are at high risk for endocarditis, your healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics. Take them before you go to the dentist or have surgery. You’re at higher risk if you’ve had endocarditis before, had a valve replaced or have had a specific heart problem since birth. You can get heartworm more than once, so be on the lookout for symptoms.
(Disclaimer : The purpose of this health-related article is to wake you up and aware of your health and to provide health-related information. Your doctor has a better understanding of your health and there is no substitute for their advice.)