Many sufferers of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy exhibit few, if any, symptoms, which makes it common for the condition to go misdiagnosed. However, in a tiny percentage of those with HCM, the thicker heart muscle might result in breathlessness, chest discomfort, or modifications to the electrical activity of the heart, which can lead to deadly arrhythmias or sudden death.
Definition, Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment Options
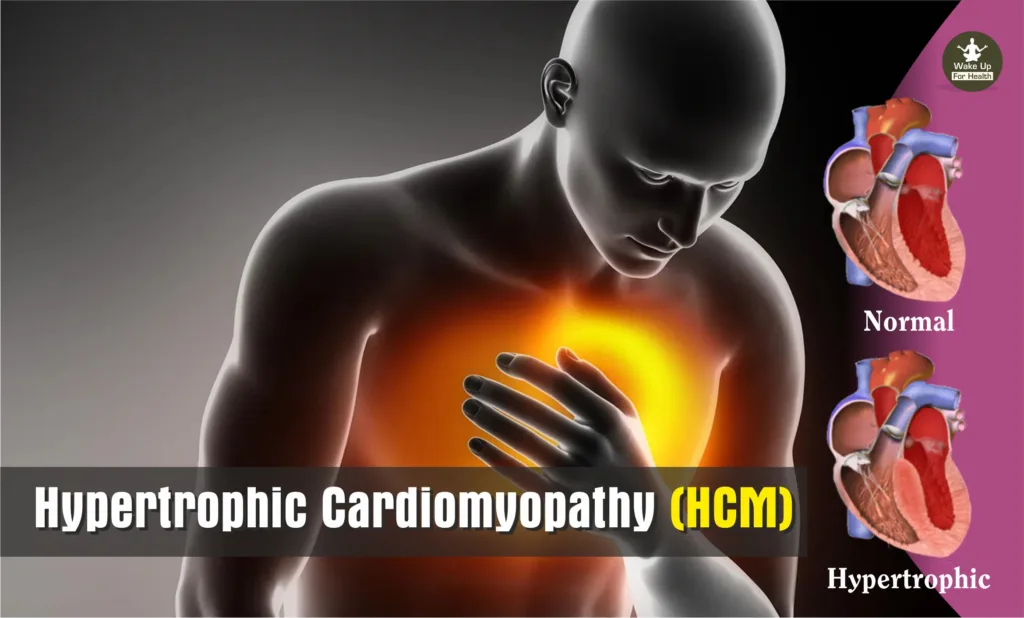
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a disease in which the heart muscle becomes abnormally thick (hypertrophied). In this condition, there is a problem in pumping blood to the heart.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is often undiagnosed because people with the condition have few or no symptoms and lead normal lives without any significant problems. However, some people with HCM may develop shortness of breath, chest pain, or other heart-related problems due to the weakening of the heart muscle, which can lead to abnormal heart rates or even sudden death.
Signs and Symptoms of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM).
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can cause one or more of the following signs and symptoms:
- Chest pain, Especially during Exercise.
- Fainting, Especially during exercise or after Extreme Exertion.
- Heart Murmur, the sound of rapid flow of blood inside the heart.
- Palpitation (Irregular Heartbeat due to any activity, Overexertion or illness).
- Shortness of Breath, especially during exercise.
Causes of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is usually caused by a mutation or mutation in a gene that causes the heart muscle to become abnormally thick.
There are a total of four chambers (two above and two below) in the human body. In these, the muscular wall (septum) between the lower two chambers becomes thicker than normal, due to which the flow of blood starts to block. This is called obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. If there is nothing blocking the blood flow, the condition is called non-obstructive-hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (NOHC).
Also in people with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, heart muscle cells (Myofiber Dysarray) become disorganized. This condition may trigger irregular heartbeat in some people.
1. Uncontrolled or Long Term Heart Disease
High blood pressure can cause structural changes in our heart muscles over time, changing the way they function. Heart attack also damages our heart muscles. Long-term rapid heartbeat (Tachycardia) and dysfunction of the heart valves are potential threats to changing the way our heart functions.
2. Metabolic Disorders
Many biochemical processes go on in the body. Due to obstruction in these processes, we have to suffer from metabolic disorders like diabetes, obesity and hypothyroidism. If control is not found on these, then it can become the cause of cardiomyopathy in the future.
3. Alcohol Addiction
Addiction to Alcohol can harm our liver and it is not good for our heart either. Excessive consumption of alcohol increases the level of triglycerides (fats in the blood) in our body. Apart from cardiomyopathy, it can also cause high blood pressure, heart failure and stroke.
4. Some Medicines
Unfortunately with every medicine there is a tail of side effects. Some of them, especially cancer drugs, are cardiotoxic – damaging to the heart muscle. Even if they are not used properly. When the doctor prescribes you any medicine, it is a better option to know its side effects.
Also A Good Read: Periodontitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Treatment
5. Some Other Diseases
Certainly some diseases have a direct effect on the structure and functioning of the heart. For example, sarcoidosis causes small lumps to form in the heart muscle. Amyloidosis, on the other hand, causes accumulation of abnormal proteins in our heart muscles.
How is Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Diagnosed?
In addition to the signs and symptoms, the doctor may also examine the medical history:
1. Echocardiogram.
Echocardiogram is usually performed to diagnose hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. This test uses sound waves (ultrasound), with the help of which it can be known whether the heart muscle is abnormally thick or not.
2. Electrocardiogram ( ECG or EKG)
This is a test that tells how the heart is working by measuring the electrical activity of the heart.
3. Cardiac MRI
In this test, pictures of the heart are created using powerful magnets and radio waves. By looking at these pictures, the doctor can tell about the muscles of the heart and how the heart and heart valves are working.
Treatment For Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
The goal of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy treatment is to relieve symptoms and reduce the risk of sudden death. The treatment of this condition depends on the severity of the symptoms.
Medicines :
Medicines can help reduce the strain on the heart muscle and normalize the heart rate. By taking these medicines, the heart is able to pump blood in a better way. Medications used to treat Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy may include:
1. Beta blockers such as Metoprolol, Propranolol or Atenolol
2. Calcium channel blockers such as Verapamil or Diltiazem.
3. Heart rhythm drugs such as Amiodarone or Disopyramide.
4. Medicines like blood thinners such as warfarin, dabigatran, rivaroxaban or apixaban can be given to prevent blood clots.
Apart from medicines, some surgeries are also available, whose names are as follows:
- Septal myectomy
- Septal Ablation
- Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator
There are many medicines available for Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (Thickening of the Heart Muscle). All these medicines are given above. But keep in mind that Please do not take any medicine without consulting the doctor. Taking medicines without doctor’s advice can cause serious damage to your health.
(Disclaimer: This article is for general information only. It is just to wake you up for your health purpose. Out intension is not to mislead or It cannot in any way be a substitute for any medicine or treatment. Always contact your doctor for more details.)
F.A.Q.
Question 1 : How serious is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Answer : As HCM progresses, it can cause other health problems. People with HCM are at higher risk for developing atrial fibrillation, which can lead to blood clots, stroke and other heart-related complications. HCM may also lead to heart failure. It can also lead to sudden cardiac arrest, but this is rare.
Question 2 : How long can you live with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Answer : Research has shown that with proper treatment and follow-ups, most people with HCM live a normal life. A database of 1,297 patients with HCM from the Minneapolis Heart Institute Foundation identified that 2% of the patients can live past 90 years, and 69% of them were women.
Question 3 : Is walking good for Cardiomyopathy?
Answer : Walking helps congestive heart failure patients in several ways: Reduces heart attack risk, including cutting the risk of having a second heart attack. Strengthens their hearts and improves lung function. Long term, aerobic activity improves your heart’s ability to pump blood to your lungs and throughout your body.
Question 4 : What foods should I avoid with cardiomyopathy?
Answer : Avoid cured and processed meats, which are high in sodium. Burgers and steaks, even unseasoned, present their own problem: they’re high in the types of fat that can lead to clogged arteries. Instead, aim to eat more fish than red meat, especially salmon, tuna, trout, and cod.
1 thought on “Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment”