Oval or round shaped harmless lump of fatty tissue located between the skin and the underlying muscle layer. Lipomas are like balls of dough, they are easily moved by pressing with fingers or palm and they are not painful. They can appear anywhere on the body but most commonly appear on the back, torso (trunk), arms, shoulders, and neck.
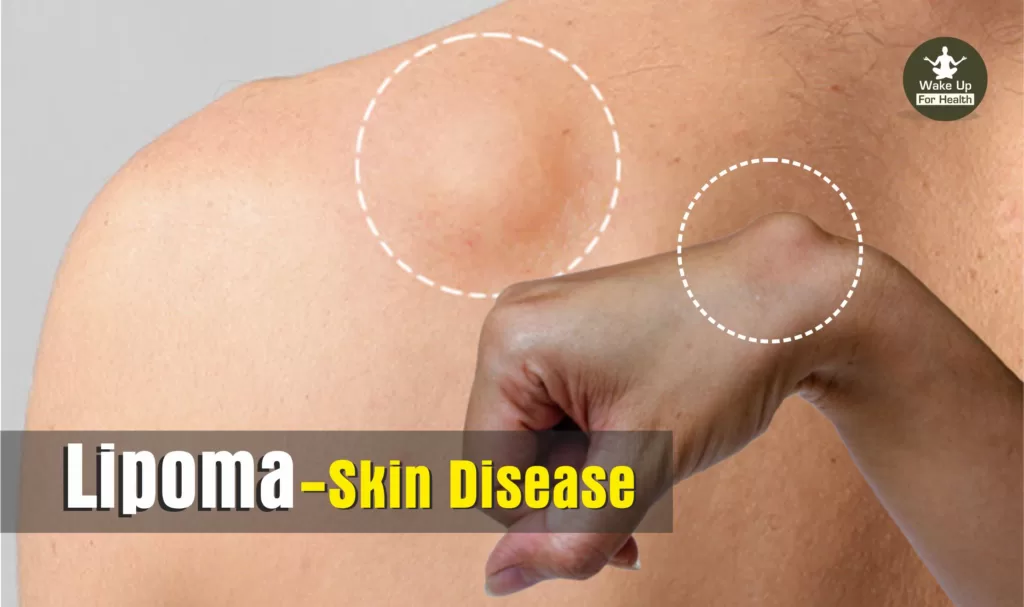
Lipomas grow slowly and most are not cancerous. In most cases, lipomas are relatively small and heal without the need for any treatment. Lipoma is also known as ‘Lump of Fat’. Let’s read about lipoma, its representation by pictures, know more about its Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention Etc.
What is Lipoma?
A Lipoma is a harmless oval or round shaped lump of fat that grows under the skin. They grow slowly and most are not cancerous can form on any part of the body, but most commonly appear on the neck, shoulders, forearms, hands, and thighs. Lipomas can develop in a person of any age group, but mostly they appear in persons aged 40 to 60 years.
Types of Lipoma
In most cases, Lipomas are harmless, but the condition can present differently depending on how the Lipoma formed. There are several types of Lipoma, including:
1. Angiolipoma
These contain fat and blood vessels (veins). They are usually painful.
2. Conventional
These are the most common type of Lipoma. These contain white fat cells.
3. Fibrolipoma
They are made of Fat and Fibrous Tissue.
4. Hibernama
They are made up of brown fat cells which help in regulating body Temperature.
5. Myelolipoma
These are made of fat and the tissues that produce blood cells.
6. Spindle Cell
In these, the fat cells are longer than they are wide.
7. Pleomorphic
These consist of fat cells of different sizes and shapes.
Symptoms
Usually, painless, but they can cause discomfort if they press on a nerve or develop near a joint (such as the knee or elbow). Most people who develop do not experience any symptoms. However, the following signs and symptoms of lipoma can be noticed:
1. Painless
Most are painless. They become painful and cause discomfort depending on their location, size and pressure.
2. Shape
Lipomas are lumps of fat, they have a rubbery texture, usually oval or round in shape and most of them are similar.
3. Movement
Because lipomas are just below the surface of the skin, they tend to move when touched.
4. Encapsulated
Lipoma does not spread to the surrounding tissue.
5. Small size
Most lipomas are small in size (less than 2 inches in diameter). However, in some cases, the lipoma can be large and can be up to 6 inches wide.
CAUSES OF LIPLOMA
The exact cause of lipoma is unknown. They are inheritable, which means they are inherited from parents or grandparents. However, certain conditions can also lead to the development of lipoma in the body. These conditions include:
1. Decrum’s Disease
A rare disorder that causes the development of painful lipomas on the arms, legs, and trunk. This disorder is also known as adiposis dolorosa or Ender’s syndrome.
2. Hereditary Multiple Lipomatosis
A hereditary illness that is passed down via families. Additionally called multiple familial lipomatosis, this condition.
3. Gardner Syndrome
Gardner syndrome or familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) causes multiple lipomas and various other health problems.
4. Madelung’s Disease
This condition is often seen in men who drink alcohol excessively. Also known as multiple symmetric lipomatosis, this disease results in the development of lipomas around your neck and shoulders.
Prevention For Lipoma
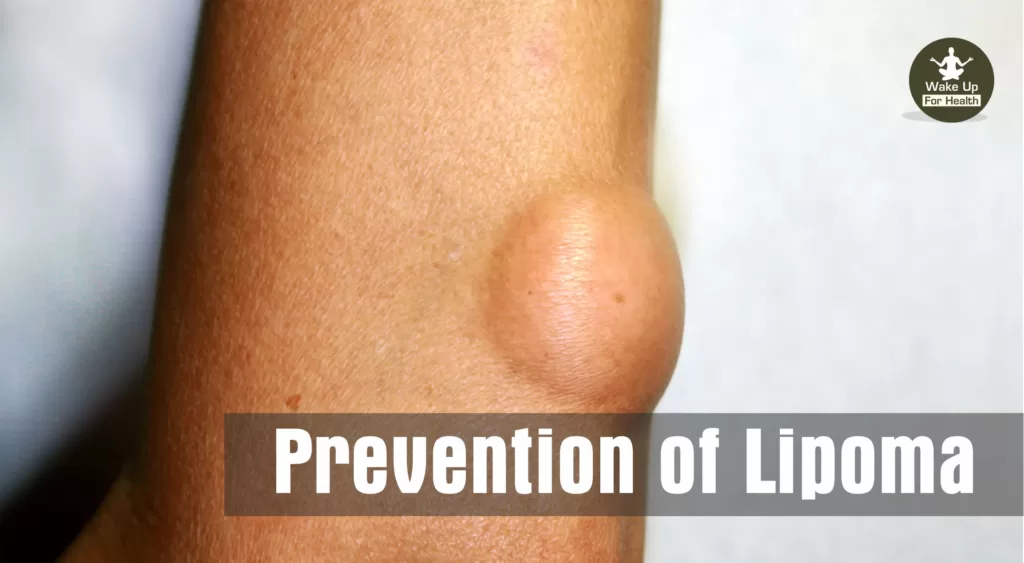
Lipomas are hereditary. Because they are passed down through families, it is impossible to stop them. However, you can reduce your risk of developing lipoma by practicing the following measures:
- Reduce obesity
- Avoid consumption of alcohol
- Seek immediate medical treatment to cure diseases that increase the risk of lipoma
- Maintain the cholesterol level in the body
- Avoid a sedentary lifestyle
- Exercise regularly
How is Lipoma diagnosed?
Primary physicians will usually be able to diagnose a lipoma by physical examination. The doctor will do a complete examination by touching the lipoma. The doctor may also recommend the following tests to confirm the presence of lipoma, if necessary:
1. Patient History
The doctor asks some questions to know about the medical history of the patient. The patient may have to explain all his symptoms and give a detailed summary of his illness to the doctor.
2. Clinical Examination
Doctors may look for characteristic “slippage signs” when evaluating a patient’s body for a lipoma. This signal is obtained by gently sliding the fingers along the lipoma edges. Lipomas tend to be mobile, small, and soft, and tend to slip under the fingers naturally.
3. Clinical Investigation
When a lipoma becomes painful or abnormally large, or if it reveals any other complication, the doctor may recommend the following tests:
4. Biopsy
A sample of the fat lump will be taken and examined under a microscope. This sample is taken to check for signs of cancer.
5. Ultrasound Scan
Sonography scan is done to find out if the lipoma is not putting pressure on the nerves or blood vessels.
6. MRI and CT scan
Lipoma treatment without surgery.
Steroid Injection:
The doctor will give a steroid injection directly at the site of the lipoma. This will help shrink the lipoma but will not cure or eradicate it.
Surgical Treatment of Lipoma
When lipoma becomes complicated or symptomatic, doctors suggest surgery. The following are the surgical procedures performed to treat lipoma:
1. Lipoma Surgery
Most lipomas are surgically cut out and removed.
2. Liposuction
This procedure is a cosmetic surgery that is used to remove unnecessary fat from specific areas of your body.
Diet for Lipoma
Lipoma can develop at any age. A person’s daily diet and lifestyle play an important role in lipoma development. Mentioned below are some dietary habits that a person should adopt when having lipoma.
1). Eat homemade food and keep in mind that the amount of fiber in the food should be high and low fat protein should be included.
2). Cut down on sugar intake.
3). Consume apple cider vinegar as it contains acetic acid which prevents accumulation of fat in the body.
4). Consume ginger and raw honey.
5). Eat more foods rich in omega 3, such as walnuts, flaxseed, chia seeds, and salmon, as they contain healthy fats and have anti-inflammatory properties.
6). Avoid fast and processed food as they contain unhealthy fats like trans fat.
(Disclaimer: This article is for general information only. It is just to wake you up for your health purpose. Out intension is not to mislead or It cannot in any way be a substitute for any medicine or treatment. Always contact your doctor for more details.)
4 thoughts on “Lipoma Explained: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Diet – WFH”