Lyme disease, also known as Lyme Borreliosis, is an infectious disease. Lyme disease is caused by the bite of a bacterium Borrelia Burgdorferi. You must have heard a lot about Lyme disease in the past. The reason for this is that this infection is spreading a lot.
Now the question arises that what is Lyme disease, what are the symptoms of Lyme disease and how does it spread and what is treatment for Lyme Disease.
Along with this, it is also necessary to get complete information about how Lyme disease can be avoided or what should be done to prevent it. So let’s know everything about Lyme disease, what happens, how it happens, what are the preventive measures and treatment.

What Is Lyme Disease or Lyme Borreliosis?
Lyme disease is an infectious disease caused by the bite of the bacterium Borrelia Burgdorferi. Lyme disease is spreading very fast. According to the news a few years ago, the name of Lyme disease was included in the fastest spreading infections in America after AIDS.
Apart from this, cases of Lyme disease are also being seen in Asia, Europe, and South America. In fact, Lyme disease is an infection associated with inflammation and redness of the skin, which occurs in humans due to the bite of Borrelia Burgdorferi. Borrelia burgdorferi are very small organisms, which stick to our skin and suck blood, due to which the infection spreads.
What is Causes For Lyme Disease?
Lyme disease is caused by the bite of Borrelia Burgdorferi. Borrelia burgdorferi are very small organisms, which stick to our skin and suck blood, due to which the infection spreads.
Must Know About Skin Diseases.
- Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) is a skin allergy. Know More About AD (Atopic Dermatitis)?
- Lipomas are like balls of Dough. What is Lipoma Skin Disease?
What are Symptoms For Lyme Disease?
Lyme disease is caused by the bite of an insect named Borrelia Burgdorferi. These insects are so small that it is difficult to see them. Symptoms of Lyme disease start appearing in humans within 3 to 30 days after being bitten by an infected insect. Know at a glance about the symptoms of Lyme disease-
What are Early symptoms of Lyme Disease?
The initial symptoms of Lyme disease may develop three to 30 days after being bitten by an infected insect.
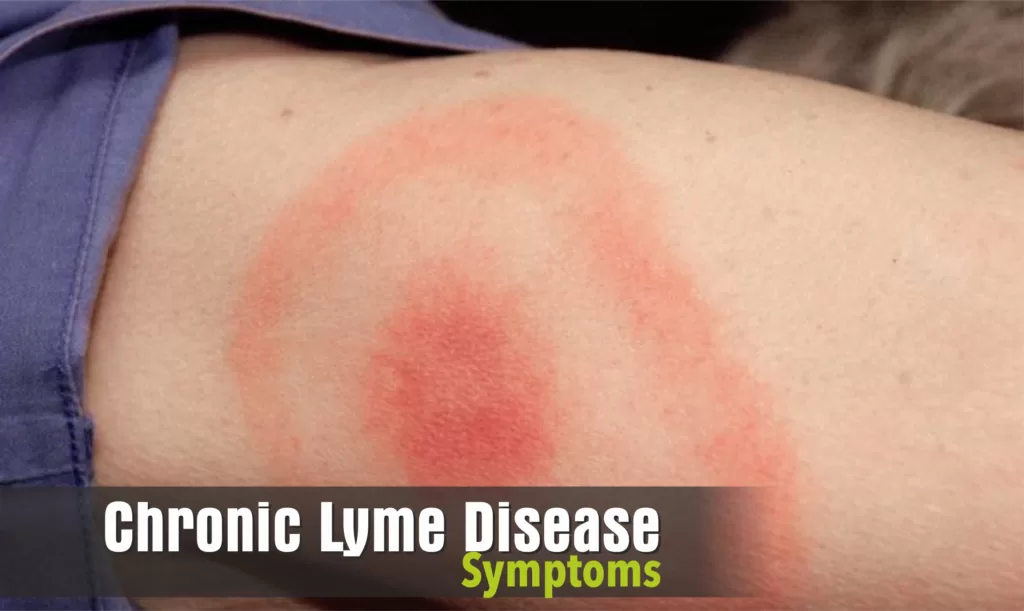
A rash appears at the site of the insect bite and sometimes looks like a bull’s eye on a dart board. The affected area of skin is red and feels slightly raised to the touch.
The rash can range in size from 2 cm to 30 cm (0.7 to 12 in) and may increase in size over several days to a few weeks in most people. In many people, the rash is the only symptom of Lyme disease.
Some people initially have flu-like symptoms such as:
• Exhaustion
• Muscle pain
• Joint pain
• Headache
• Fever or shivering
• Stiff neck
What are Later Symptoms of Lyme Disease?
If it is not treated then there can be serious problems later on. It can also affect the joints, nerves and in some cases the heart.
If you experience any of the following symptoms, seek medical help:
1. Joint Pain
Some individuals may complain of inflammatory arthritis (swelling and pain in the joints). But even if symptoms like joint pain are left untreated, they get cured on their own.
2. Neurological Symptoms
Neurological Symptoms (those that affect the nervous system) may include:
- Numbness and pain in your limbs
- Partial paralysis of the muscles in your face – usually affecting one half of the face (sometimes called Bell’s palsy)
- Weak memory
- Trouble concentrating
- Change in personality
- In some rare cases, people get a type of bacterial meningitis. This is a serious condition in which the meninges (the protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord) become inflamed. Its symptoms are:
• Severe Headache
• Stiff Neck - Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
Must Know About Skin Diseases.
Heart Related Conditions
In rare cases, untreated Lyme disease can lead to inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis).
Myocarditis can cause irregular heartbeat and sometimes blockage in the heart.
Symptoms include:
- Breathlessness
- Fainting
How to Diagnose Lyme Disease?
Lyme disease is a disease that is difficult to diagnose, especially in the later stages. That’s because its symptoms are similar to those of more common diseases, such as infections and arthritis.
A pink or red bull’s eye rash is important in diagnosing Lyme disease, and about 90 percent of people develop the rash within 30 days of being bitten.
Be sure to tell your doctor if you haven’t had a rash but are experiencing symptoms late in Lyme disease, such as joint pain or flu-like symptoms, if you’ve spent time in an area with dense trees or shrubbery.
If it is likely that you have been bitten by the insect, your doctor may order tests to confirm or rule out Lyme disease.
Tests to Diagnose Lyme Disease.

Testing for Lyme disease needs to be done a few weeks after the insect bite because it takes that long for the infection to develop. If the symptoms of Lyme disease are visible even after the negative report, then there will be a need to get the test done again.
The tests used to diagnose Lyme disease are:
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Test
- Western Blot Test
1. ELISA Test
The first type of blood test is known as the Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) test. This test checks for specific antibodies produced by your immune system to kill Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria.
The ELISA test is not 100% accurate because it can sometimes give a positive result (this is called a false-positive result) even if you do not have Lyme disease. This can happen if you are having symptoms because of another condition. Such as syphilis, glandular fever or rheumatoid arthritis.
Because of this, a positive ELISA test is followed by a Western blot test.
2. Western Blot Test
In the western blot test, a small sample of blood is taken. The proteins present in the blood are separated and placed on a thin sheet made of permeable material. The proteins are then studied for antibodies used by the immune system to fight off the Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria that cause Lyme disease.
Lyme disease can be confirmed if both the ELISA test and the Western blot test result positive.
What are Complications For Lyme Disease?
- If Lyme disease is not treated on time, it increases the risk of heart diseases.
- If Lyme disease is not treated on time, it can also cause joint pain.
What are Risk Factors of Lyme Disease?
Lyme disease usually occurs in children between the ages of 5 and 14 and adults between the ages of 40 and 50. The most substantial risk factors for Lyme disease are high-risk areas where contact with ticks can occur easily – such as the New England states, as well as Minnesota and Wisconsin. Other risk factors for Lyme disease include outdoor activities such as gardening in the woods or fields that put you at higher risk of Lyme disease.
What are the Stages of Lyme Disease?
There are 3 stages of Lyme disease have been considered.
Stage 1 of Lyme Disease:
Symptoms of Lyme disease in the first stage include fever, chills, or a rash along with skin swelling.
Stage 2 of Lyme Disease:
In the second stage of this disease, the disease spreads to the nervous system. It can have palsy and meningitis.
Stage 3 of Lyme Disease
The third and final stage of Lyme disease is considered dangerous. In this stage, the infection spreads a lot and a complaint of swelling in the brain or arthritis can be formed.
What are the Preventions For Lyme Disease?
There is currently no vaccine available to treat Lyme disease. A vaccine was developed in the US in 2002, but was not used due to side effects.
The best way to prevent Lyme disease is to protect yourself from being bitten by these insects when you walk around trees or shrubs that may be prone to Lyme disease. The following precautions can protect you from Lyme disease:
- Wear long-sleeved shirts.
- Tuck your pants into your socks.
- Use insect repellant.
- Check yourself for insects stuck on the body.
- Check the body of your children and pets for insects.
If you find an insect on your or your child’s skin, grasp it gently and pull it off as close to the skin as possible. It would be better to use a sharp toothed tweezer for this.
Never use a lit cigarette, match stick or essential oil to remove it.
Where are these Insects found?
These insects can be found in dense or overgrown vegetation where they can reach the animals from which they get their food.
Although they usually occur in places with woods and shrubs, they can also occur in gardens or parks where such vegetation is present.
Read Also : Trigeminal Neuralgia : This disease is also called suicide disease.
Who are at more risk for Lyme?
Those at greater risk of Lyme disease are those who visit wooded areas and bush areas and participate in activities in these areas. For example:
- Campers
- Hikers
- Farmer
- Forest worker
- Soldier
- Gamekeepers
- Most insect bites occur in the late spring, early summer, and fall, as this is the time of year when people participate in outdoor activities such as hiking and camping.
Treatment for Lyme Disease?
Oral antibiotics (tablets, capsules, and liquid) are recommended for the treatment of Lyme disease. Most people have to take a course of two to four weeks depending on their condition.
If you have been prescribed antibiotics, you must complete the course even after you feel better as this will ensure that the bacteria is completely gone.
Antibiotic injections (intravenous antibiotics) may be used if your symptoms are mild and arthritis or neurological problems are occurring.
Most people with later symptoms of Lyme disease need to take intravenous antibiotics.
Some antibiotics (both oral and intravenous) used to treat Lyme disease can make your skin sensitive to sunlight (photosensitivity). You should check the leaflet that comes with the medicine to see if this can happen. Avoid prolonged exposure to the sun and do not use tanning devices until the course is completed.
(Disclaimer: This article is for general information only. It is just to wake you up for your health purpose. Out intension is not to mislead or It cannot in any way be a substitute for any medicine or treatment. Always contact your doctor for more details.)
1 thought on “Lyme Disease – Lyme Borreliosis Disease? Symptoms, Causes, Treatment and Prevention”